MDPI Articles Cited in the News: November 2025
MDPI publishes research across a diverse range of scientific topics. With over 500 mentions from news outlets throughout November, we highlight some of MDPI’s science mentioned by reputable media outlets such as TIMES, The Guardian, The Conversation and USA today.
Here, we learn about the staggering effect that the human microbiome can have on cognitive health and how important natural environments are for early development. We also see how red meat can be an important source of protein, and why stigma can discourage people with dementia from seeking the help they need.
The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders
Mentioned in TIME | Published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences (IJMS)
The human microbiome can have a significant impact on health and disease. A review published in IJMS explores the correlation between our microbiome and how it can affect cognitive functioning – specifically in the context of psychiatric disorders.
The insightful study demonstrates just how powerful the gut microbiome can be through its impact on human brain function by processes such as immune responses, neurotransmission, and even hormone regulation.
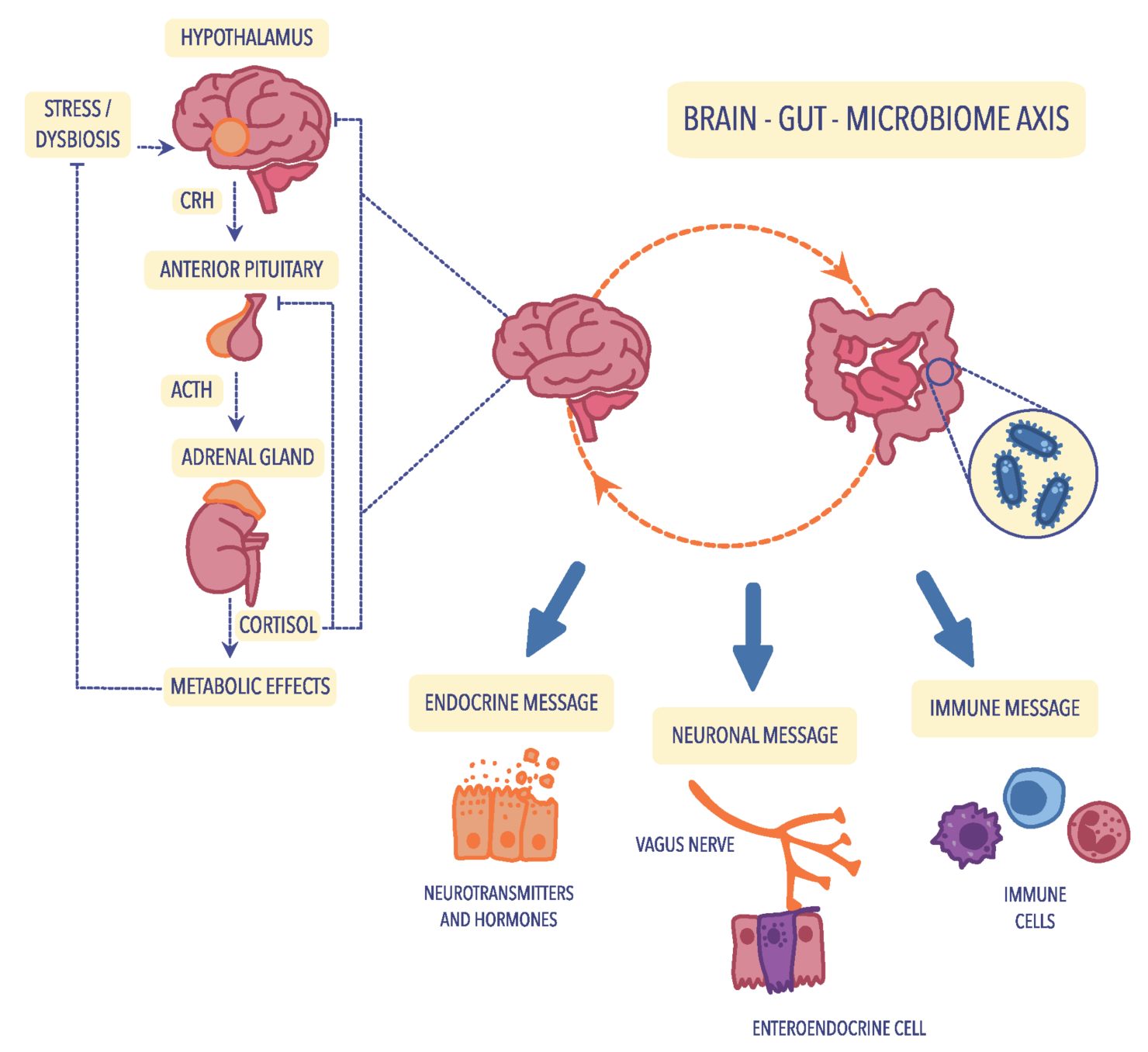
The authors discuss the role of microbiota alterations in the development of psychiatric disorders such as major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Optimising Early Childhood Educational Settings for Health Using Nature-Based Solutions: The Microbiome Aspect
Mentioned in The Guardian | Published in Education Sciences
Early childhood development is a critical period of physical, cognitive and social development for children, and can be impacted by many factors, including their physical environments.
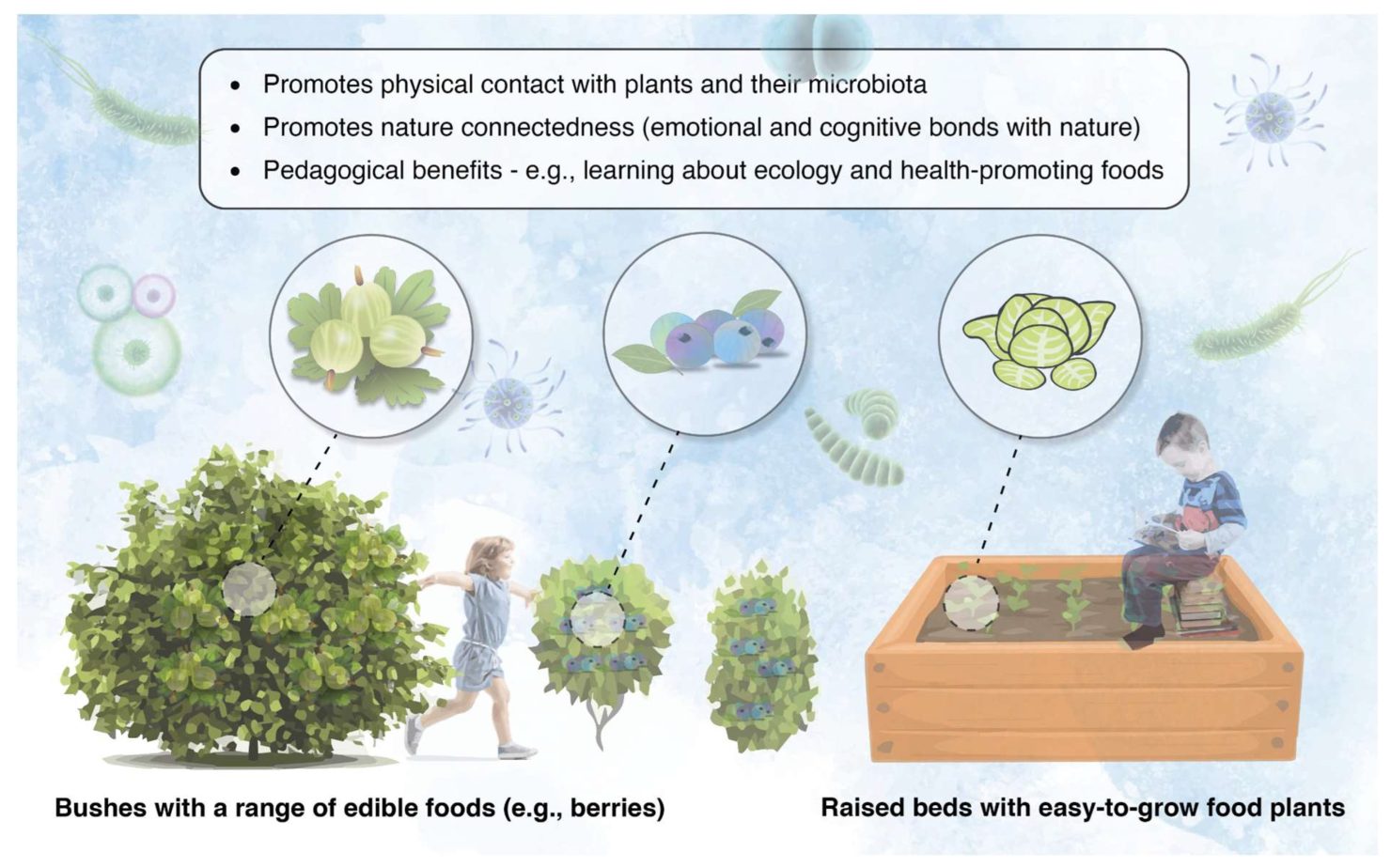
Exposure to natural environments is important for children and can be immensely beneficial for their health and well-being during their early development. A perspective article published by researchers from Australia emphasises the importance of instilling nature-based practices and exposing children to natural environments. Here, they discuss how this interaction with the environmental microbiota can support and optimise human health.
They provide practical methods of integrating nature interactions and environmental knowledge into education settings for children in their early years. Additionally, the authors urge the relevant bodies to adopt a ‘One Health Perspective’ – this is a holistic approach ensuring that human and animal health and the environment are interconnected, to ultimately benefit all.
This approach encourages children to develop a sense of connection and care for the environment, also fostering an awareness of their own health and nutrition to benefit their later years and future communities.
Within My Walls, I Escape Being Underestimated: A Systematic Review and Thematic Synthesis of Stigma and Help-Seeking in Dementia
Mentioned in The Conversation | Published in Behavioral Sciences
Dementia is an umbrella term given to describe the condition caused by diseases like Alzheimer’s. The key characteristics of the condition include memory loss and other cognitive deficits that can significantly impact daily life. It can be immensely challenging for those experiencing the condition, as well as for the people around them.
A review published in Behavioral Sciences provides important insights into the difficulties that people with dementia experience due to stigma and stereotypes associated with the condition. The key themes of the challenges included:
- Reluctance to disclose the condition
- Internalisation or rejection of stigmatizing beliefs
- Influence of family and community
- Attitudes of healthcare professionals
- Lack of awareness in the broader society.
Furthermore, factors such as their loss of autonomy, limited access to appropriate services, and a lack of peer support contributed to the stigma.
Social stigma can be significantly influential on people with dementia being able to seek the help they need to cope with their condition. The systematic review demonstrates the present need to address the stigma associated with people with dementia, and for frameworks to be established to help mitigate their impact.
Practical frameworks include providing more training across healthcare professions, campaigning to promote social awareness catering to different cultures and demographics, reformation of key policies, and delivering additional support to carers.
Red Meat Amino Acids for Beginners: A Narrative Review
Mentioned in The Independent | Published in Nutrients
Red meat is a major source of protein; however, its overconsumption has also been implicated in the development of various cardiovascular and metabolic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer.
Red meat includes beef, pork, lamb, veal, and also includes processed meats like ham and salami, making it a large portion of the typical Western diet. A review published in the Open Access journal Nutrients notes that while red meat has been shown to contribute to the development of disease, there are a few factors that need to be considered. This includes the method of preparations of the meat – for example, some methods involve the production of carcinogens while others do not.

The authors highlight the value of red meat being a good source of essential amino acids and dietary fats for both pregnant women and older adults. Future research would entail the impact of red meat on health and understanding the exact mechanisms by which red meat contributes to disease.
In addition, development of better guidelines on how to best to incorporate red meat into a healthy diet is important to help people make more conscious choices when consuming meat.
To read more, access MDPI’s full journal list