MDPI Papers Cited in the News: August 2024
In this month’s Cited in the News, we take a glimpse into the world of healthcare. Here, we understand how microplastics might be harmful to us, the effect of the Western diet, and how looking after mental health is essential in breast cancer survivors. We also dip into environmental research, where we see how rice terraces in China can help water systems and conservation practices.
With MDPI’s open-access articles cited in prominent news outlets such as The Guardian and BBC Future, this article covers range of interesting topics selected from the 889 news mentions from this August.
The problem with plastic
Cited in The Guardian
Published in Antioxidants
Microplastics (MPs) have garnered significant attention in recent years. This is due to its significant environmental and potential health impacts. Recent studies attempt to understand the effects that microplastics have on health, and mechanisms that contribute to potential adverse effects. A 2024 review published in Antioxidants and cited in The Guardian provides a comprehensive update on the current understanding of microplastics and their effect on oxidative stress (OS).
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an increase in radical oxygen species (ROS) in the body, and not enough anti-oxidants to balance it. This leads to molecular and cellular damage, which could lead to further damage to tissues and organs.

Sources that increase ROS and OS include UV radiation, pollution and diet. Research now shows that microplastics may also induce increased OS in the body. As the authors discuss:
‘Oxidative stress is one of the most frequently reported negative effects that may result from exposure of MPs.’
In the review, the authors summarise the effects that MP has on cellular integrity, including how they affect the DNA and other cellular organelles. The review offers a perspective, concluding that MP does have toxic effects on organisms through the induction of OS in the body. The presence of MP can ROS can result in inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death, increasing OS and hence may have detrimental effects on other tissues and organs.
The authors also discuss how there needs to be a deeper understanding on molecular mechanisms of MP toxicity. They further state how there is a need for more epidemiological and clinical data to assess the adverse side effects of MPs.
Depression in breast cancer survivors increases mortality rates
Cited in U.S. News
Published in Brain Sciences
Depression is a mood disorder that can affect people of all backgrounds and can be debilitating to live with. There are different types of depression, one of which includes major depressive disorder, otherwise known as clinical depression. This can impact many aspects of one’s life, making it difficult to function normally and carry out day-to-day activities. According to previous studies, depression is associated with an increased risk of mortality in adults in the U.S.
Serious physical illnesses, such as developing cancer, can impact mental health and can increase the risk of having depression. An article published in Brain Sciences and cited in The U.S. News analysed the risk of mortality of breast cancer survivors with clinical depression. The study states how mental illnesses, including depression, are receiving ‘extensive attention in the published literature,’ indicating its importance as a comorbidity.
Through a population-based data analysis, the study found that those who survived breast cancer and developed depression had significantly increased mortality rates. These findings emphasise the importance of mental health in cancer patients, and the need to address this public health issue by the government and healthcare systems so that people experiencing depression are getting all the support they need.
Is the Western diet bad for you?
Cited in CNN
Published in Nutrients
The Western diet mainly consists of food that is high in salt, fat and sugar. It also includes fried food, red meat and ultra-processed food items. Research shows that a diet containing a high amount of ultra-processed food is associated with negative health effects. A review published in Nutrients analyses these impacts on metabolism and overall health.
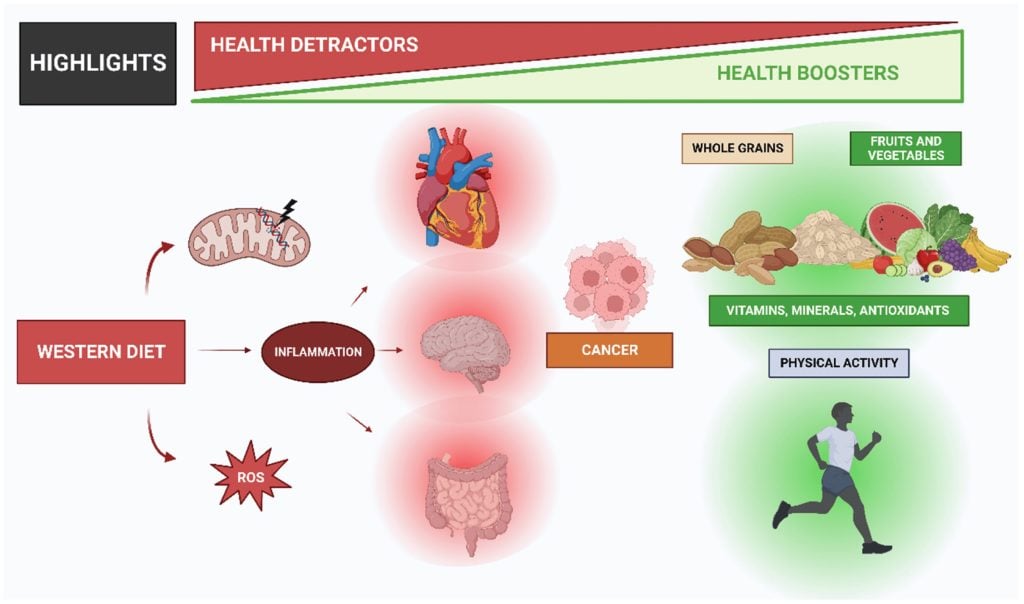
By exploring data from previous studies, the study describes the negative effects of the Western diet on different aspects of health. The review includes a thorough explanation of how the diet influences metabolism, gut microbiota, inflammation, mitochondrial function, cardiovascular function, mental health and the risk of developing cancer. The authors also include practical applications to help improve outcomes, such as a reduction of ultra-processed and fast food consumption, an increased intake of fruits and vegetables and increased frequency of exercise.
Furthermore, the authors discuss the economic and social aspects that shape the way people eat and live. Food that is highly processed is usually cheaper and more convenient to access. The authors emphasise this, stating:
‘Lower-income individuals and those with less education are more likely to have poor dietary habits and be at risk for chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.’
The research is essential to understand the impact that the Western diet has on health and well-being, and the implications for public health.
Importance of Rice Terraces in China
Cited in BBC Future
Published in Water
Rice terraces in China are an important part of the region’s cultural agriculture and hydrological stability. An article published in the Open Access journal Water analyses how exactly these rice terraces in the Xinhua Basin contribute to water stability. In the study, hydrological changes caused by land use and cover change (LUCC) within the rice fields were measured in these areas.
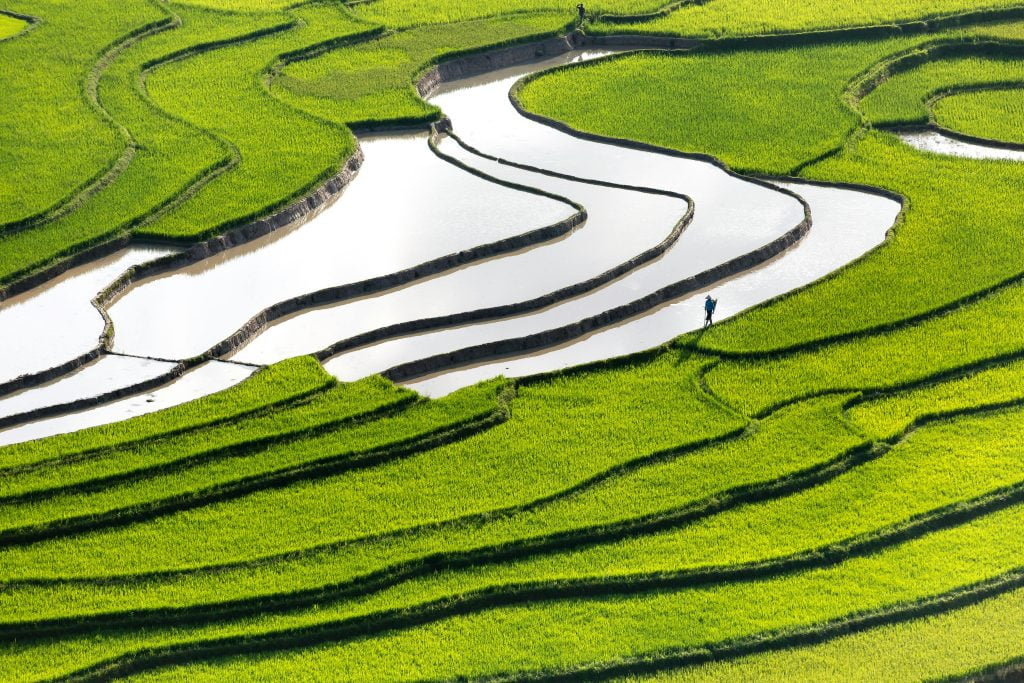

They used the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) hydrological model to assess this change over extended periods. This model analyses components such as surface runoff, return flow, groundwater flow and water transfer. The study aimed to analyse the LUCC watershed in the Xinhua Basin to analyse the hydrological impacts of the rice terraces and identify influencing factors. The authors found that rice terraces enhance the overall hydrological stability of the region. Furthermore, they found that having a higher proportion of paddy fields versus forests results in more water runoff with lower stability.
There is an urgent issue of water shortages worldwide and a global effort to increase water conservation. Research on how different water systems, including the ancient rice terrace architectures, can increase hydrological stability and maintain water conservation is vital in discovering new ways to ultimately address the issue of the global water crises. It also helps provide ideas for innovative ways to conserve water in developing urban areas.
To read more research on health and well-being and the environment, see a full list of MDPI’s Open Access journals that are free to read immediately.