Insights from MDPI Top Picks: August 2024
In this August’s roundup of top MDPI articles, we take a look at research published in a variety of journals, including Cancers, Plants and Journal of Intelligence. Here, we learn about a novel imaging technique for oral cancer diagnostics that was further developed by researchers, a newly discovered form of fungal infection impacting pomegranates in Italy and explore children’s early understanding of ruler measurements and how they learn about them. We also learn about drought patterns in the Kizilirmak Basin, and how the research creates a foundation for efficient management strategies of the extreme weather condition.
Outbreak of Alternaria Black Spot of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) in Italy as a Consequence of Unusual Climatic Conditions
Published in Plants
Climate change causes many types of disturbances. This is seen in things like extreme weather changes, increased frequency of natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes, wildfires), rising sea levels, and loss of animal life from habitat destruction. Another unusual change which has been attested to climate change is an outbreak of a new disease: Alternaria Black Spot of Pomegrante in Italy.
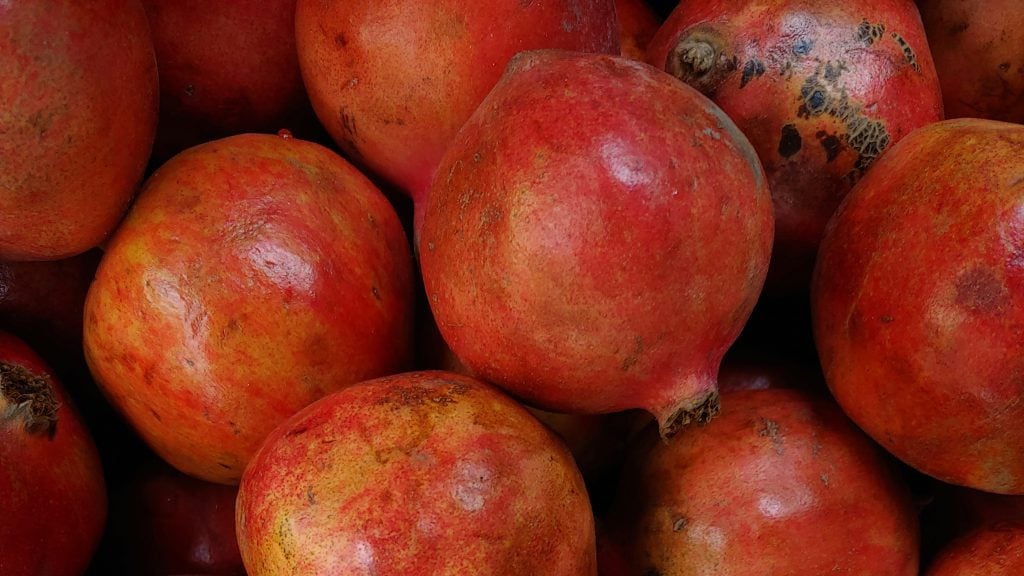

This disease is a type of new fungal infection, causing black spots and significant detriment to various fruits. In the study, the researchers determine the aetiology of the disease, explore the potential causes of the fungal disease, and look at the severity of the disease in pomegranates. Authors of the study, Tirro & Conti Taguali et al., highlight the motivation and importance of the study.
“The recent outbreaks of Alternaria diseases affecting the canopy (leaves and fruitlets) in the Mediterranean region, observed over the past two years, are becoming a significant concern for various crops, including pomegranate, carob, mulberry, and olive. These outbreaks, triggered by unusual rainfall patterns, are further exacerbated by warm temperatures and the presence of abundant young vegetation, which is highly susceptible to infection and facilitates pathogen sporulation.”
By carrying out a multigene phylogenetic analysis of four DNA regions, they were able to describe three different morphologies They also carried out pathogenicity tests on each type, to see which morphotype produced more symptoms.
“Our study on the Alternaria black spot of pomegranate not only documents the first occurrence of this disease in Italy but also highlights the urgent need to understand how shifting climatic conditions are influencing plant disease dynamics in Mediterranean crops.”
Imaging Biomarkers of Oral Dysplasia and Carcinoma Measured with In Vivo Endoscopic Optical Coherence Tomography
Published in Cancers
New cancer diagnostic technologies have been developing rapidly in the last decade, particularly in the light of advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning technology. The early diagnosis of some cancers can be life-saving. In a recent study published in Cancers, researchers present seven features for the rapid diagnosis of oral cancers.
Co-author of the study, Dr. Jeanie Malone, discusses the importance of their research, and how they used advanced technology to create these seven criteria during diagnostics
“Oral cancers are associated with high mortality in advanced stages. Early diagnosis is associated with better patient outcomes, but this is challenging to achieve as benign lesions appear similar to pre-malignancies. Multiple biopsies may be required to ensure the most pathologic tissue is sampled for accurate diagnosis.”
The researchers therefore used previously developed optical coherence tomography (OCT) endoscope technology as part of the study.
“OCT is an imaging technique that provides high-resolution, three-dimensional visualization of the first few millimetres of tissue. We have previously developed an OCT endoscope which can reach most sites in the oral cavity – but assessing large three-dimensional volumes for the most clinically relevant information is challenging even for OCT experts.”
Dr. Malone further emphasises the importance of researchers in oral cancer diagnosis.
“Leveraging an in-house deep learning segmentation tool, this paper explores seven quantitative imaging biomarkers and assesses their utility in distinguishing oral pre-cancers and cancers. Features that measure epithelial morphology (epithelial depth, loss of epithelial-stromal boundary) are identified as the best indicators of disease state.
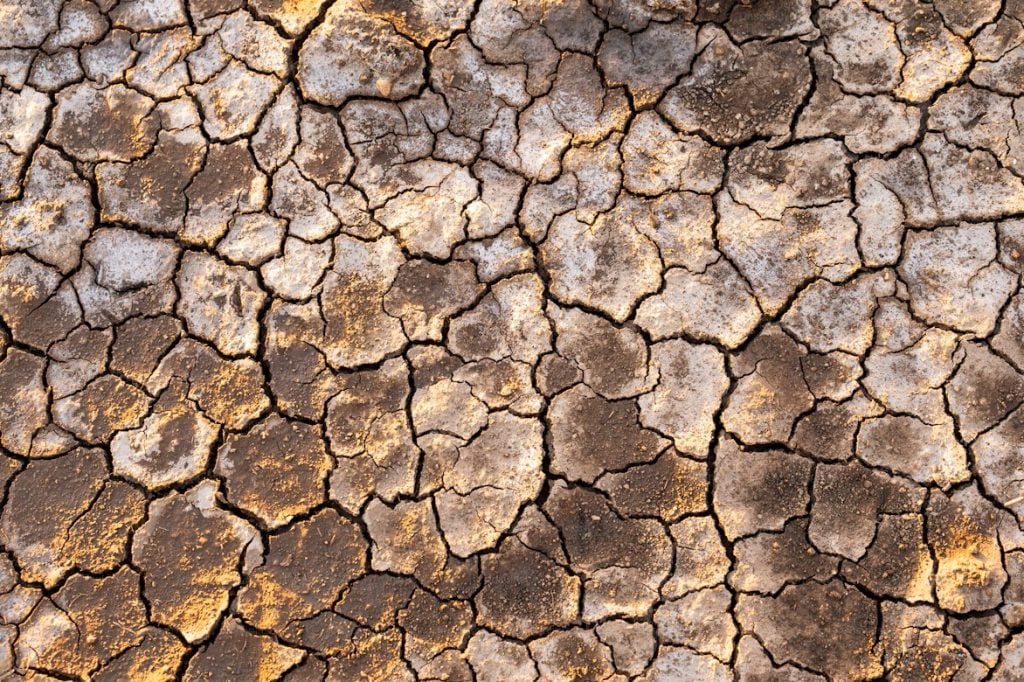
Meteorological Drought Analysis and Regional Frequency Analysis in the Kizilirmak Basin: Creating a Framework for Sustainable Resources Management
Published in Water
Along the same vein as the previous study mentioned, we also see the effects of climate change in a study analysing drought patterns in the Kizikirmak basin. Drought is an extreme weather condition which can be brought about by increasing temperatures caused by climate change. Analysing patterns of drought is important to instigate effective management strategies essential both for the environment and public health.
The study, published in Water, analysed monthly precipitation data in the basin from 1960‒2020. They then used different indices, such as the standard precipitation index, to determine various important factors, such as draught durations and mapped the geographical placement of the draughts.

Dr. Demir, co-author of the paper, describes the study carried out and the methods they used:
“Our study highlights the importance of understanding drought patterns and their potential impacts on water resources, especially in regions like the Kızılırmak Basin. By employing advanced statistical methods such as the L-moments approach and utilizing widely recognized drought indices, we have developed drought maps that can help predict drought intensities for return periods up to 1000 years.”
They also highlight the importance of drought research, and how this study can be helpful for governments for strategy development:
“This study is crucial for improving drought management and mitigation strategies, particularly in areas where long-term precipitation data may be limited. We believe that the tools and insights from this research can significantly contribute to sustainable water resources management in the face of increasing climate variability.”
Overturning Children’s Misconceptions about Ruler Measurement: The Power of Disconfirming Evidence
Published in Journal of Intelligence
Studies show that children often have difficulty understanding the concept of ruler measurement, a critical life skill used often in everyday life. A study carried out by Kwon et al. attempts to explore this and to understand why children find the concept of measurements difficult to wrap their heads around, and what can be done to help. The study mentions only a startling 29% of fourth-grade students in the USA can correctly complete measurement problems.
The study implemented three experiments to see if they could improve children’s understanding of the concept. This involved giving the children a more thorough understanding of shifted ruler items, which resulted in an increased understanding of measurement units.
Shifted ruler problems are a concept that children often do not understand – these problems entail the measurement of an object that does not start at zero on the ruler. Furthermore, the experiment also included training on children’s structural alignment, where they placed unit chips aligned with the ruler and object.
Giving cognitive strategies and training sessions to the students showed alternative strategies may be required to help children understand the concept of ruler measurement. As concluded by the authors in the study: “these findings have practical implications for how measurement instruction could be modified to increase children’s understanding of linear measurement, which, in turn, may have downstream consequences of understanding units and measurement more generally.”
To read more novel and top research published across a variety of scientific disciplines, see MDPI’s journal list for more.