The Rise of Fungi: The Last of Us
Pandemics have always been an interesting topic to explore in television and film. However, recently pandemics have become more of a reality and in turn more relevant in pop culture. It’s a great way to unwind and explore extreme situations; however, it’s also important to understand the truths behind these topics. One series that has been making headlines is an HBO max series entitled ‘The Last of Us” It’s a thriller based on a video game where a fungus infects humans causing a worldwide pandemic. This pandemic is made deadly as the fungal infection controls its victims’ brains, causing “zombie-like behavior”. Recently, Journal of Fungi (JoF) was mentioned in an online article promoting the series. It included an interview with the editor-in-chief of JoF, Dr. David Perlin.
This blog post investigates how topics such as fungus pathology have become popular in the news and how JoF is a reliable source to keep up to date with these topics.
Cordyceps
The fungus in the series is based on the fungus species Ophiocordyceps unilateralis, also referred to as Cordyceps. In reality, they can’t infect humans because they cannot survive human body temperature. In fact, they are commonly used in Chinese medicine to treat chronic kidney disease, as they are suggested to reduce creatine levels and blood sugar. Moreover, they can also be used to improve energy and sleep patterns and also increase appetite.
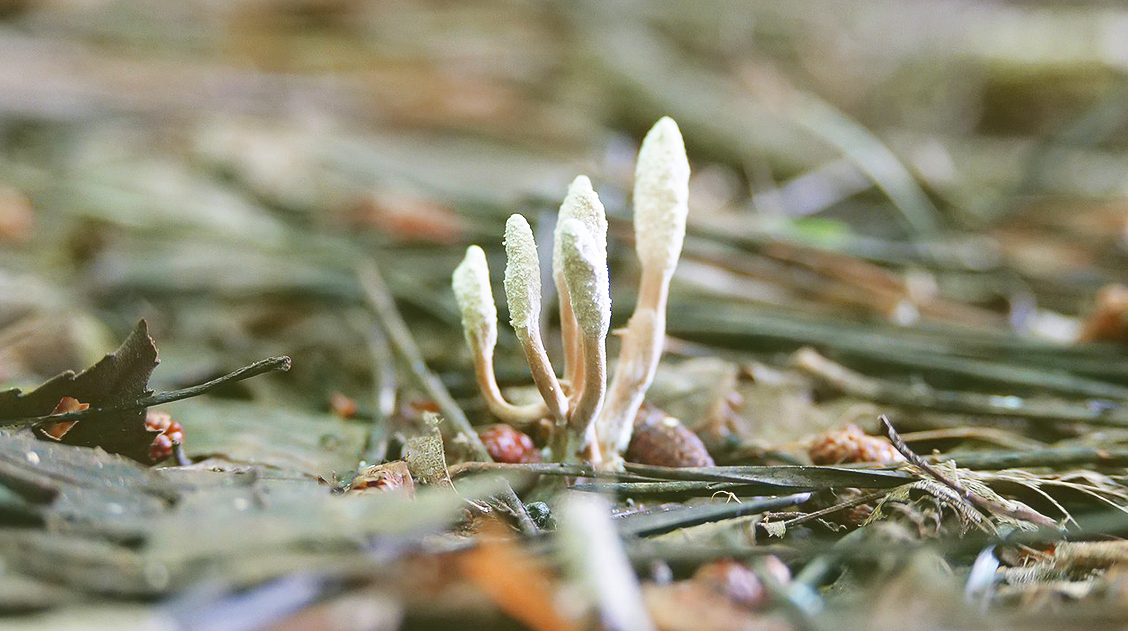
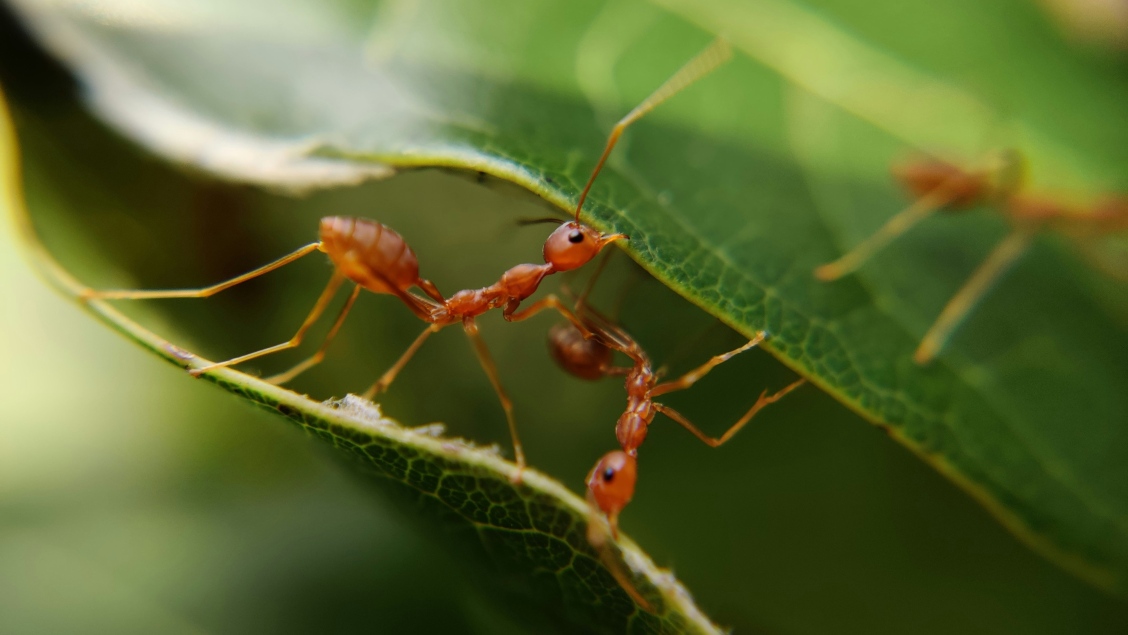
Cordyceps in insects
However, the fungus in the series is not completely unrealistic. They can and do infect ants, causing “zombie-like” effects. Their main goal is survival, to do this they must propagate and spread.
The fungus is suggested to be found in tropical rainforests. They can infect ants using their spores to penetrate their exoskeleton. As this infection sets in, it changes the ant’s behavior, influencing them to leave their nest and find favorable conditions to propagate the growth of the fungus. The fungus eventually kills the ant by growing inside of it and feeding off it.
Once the ant has died and dried up, the fungus reaches out of its head using a fruiting body. This allows it to disperse its spores and trap other ants.
Most people have their own predictions of how the human race will eventually become extinct. Many of my old microbiology and fungal pathology university lecturers predicted that bacteria and fungal pathogens would evolve quicker than humans. This would result in complete antimicrobial resistance and the extinction of the human race.
Antimicrobial resistance in fungi
Antimicrobial resistance is a huge threat to human health. It develops when microorganisms or fungi produce resistance genes against antibiotics.
Globally, it caused 1.27 million deaths in 2019. In the U.S., more than 2.8 million antimicrobial infections occur each year. As antimicrobial resistance develops into a complex health issue, it’s important to have a reliable source to keep up to date with all the new advances.
Journal of Fungi
JoF is an international, peer-reviewed, open-access journal of mycology. It has an impact factor of 5.724. The journal is affiliated with The European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM), the Medical Mycology Society of the Americas (MMSA), and the Spanish Phytopathological Society (SEF).
Because of this, their members receive a discount on the article processing charges. The journal is published monthly and has a dedicated reviewer editorial board that oversees this process.
Published papers
JoF has had a variety of mentions and overlaps of topics in various online publications and broadcasting companies. It has a history of publishing relevant and interesting studies in both culture and science.
Treatment of fungal infections
One example of this is an article entitled “Humans are not prepared for a pandemic caused by fungal infections” in National Geographic. This post suggests that antifungal resistance is increasing, which results in an increased risk of lethal fungal infections.
Journal of Fungi research
A review in JoF provides reliable studies which investigate the antifungal treatment Orlofilm as a possible solution for treatment options.
Orlofilm has exhibited activity against many molds and fungi but lacks activity against yeasts and Mucorales species. As antimicrobial resistance becomes a bigger issue, this review identifies that Orlofilm has the potential to treat invasive infections caused by resistant bacteria and fungi.
Multidrug resistant fungi
Another topic JoF published research on which has been mentioned in the news is the emerging multidrug-resistant yeast species first identified in 2009, Candida auris.
C.auris is the cause of severe human fungal infections globally and has caused havoc in hospital environments. It’s the leading cause of invasive candidiasis. Unlike other candida species, C.auris can tolerate hypersaline environments and high temperatures. Because of this, there is some concern that increases in the global temperature due to global warming may be promoting the spread of the species.
Journal of Fungi research
The study in JoF investigates what is currently known about C. auris and the gaps in research that need to be filled in order to study the pathogenesis of the fungi. Its aim is to stimulate more research in this area by identifying gaps in current research. The researchers emphasize that a global response is needed to respond to the spread of C.auris infections in hospitals and nursing homes.
Also, a focus needs to be put on the evolutionary sources of C.auris and a better overall understanding of their ecology. And how global warming is affecting the behaviors of both fungi and yeast species is also relevant.
Black Fungus
Another popular topic concerning fungi in the news has been the resurgence of black fungus infections caused by Mucormycetes.
Mucormycetes are a group of fungi that are common in the environment, mostly in soil and compost piles. Because of this most people are exposed to this type of fungi on a daily basis. These fungi are harmless to most of the population. However, they have the potential to become harmful to people with weakened immune systems.
An article published by CNN in 2021 identified that the rates of black fungus infections caused by Mucormycetes had increased since the pandemic. It describes this increase in infections as India’s second covid crisis. Because the coronavirus has weakened many of the population’s immune systems, it has given the Mucormycetes the opportunity to spread infection.
In addition, an increase in black fungus infection has been seen in other countries such as Afghanistan, Egypt, and Oman. However, it has not spread to the same extent as India. This is suggested to be because Mucormycetes feed on sugar and India has a large population with diabetes.
In fact, International Diabetes Federation has projected that by 2030 up to 98 million Indians could be diagnosed with diabetes. Black fungus infections can be lethal and they have a mortality rate of 50%. Because of this, they need to be diagnosed and treated quickly to increase the chance of survival. They can also result in permanent damage to the face and vision loss.
Journal of Fungi Research
To help to combat this, JoF published a review in 2020 where researchers collated recent information on the epidemiology and diagnostic methods for black fungus infections.
They identified that diagnosing black fungus infections caused by Mucormycetes can be challenging. This is crucial as time is critical when diagnosing and treating this infection. The researchers concluded that much more research is needed in this area, specifically to improve rapid, non-invasive testing methods.
Conclusions
Although Cordyceps are not harmful to humans like they are in the hit HBO max series “The Last of Us”, other species of fungi and yeasts do have the potential to cause serious infections. As antimicrobial and antifungal resistance increases, it’s important to have a reliable source for updates on these microorganisms. In addition, as the effects of global warming become more prevalent it’s also important to investigate ecological changes in these species and how it affects their behavior.
If you’re interested in learning more about or are interested in submitting research in Fungi and yeasts, visit JoF for more information.